Basic Outboard Maintenance: Part One
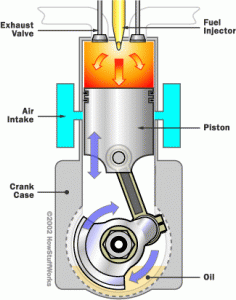
 The vast majority of outboard motor problems are easily preventable with proper care and routine maintenance. Flushing the engine after six hours of boating isn’t fun, but it will help you keep your engine performing in peak condition and extend its longevity. Although motor maintenance is a chore, it’s easy for virtually anyone with a tool kit.
The vast majority of outboard motor problems are easily preventable with proper care and routine maintenance. Flushing the engine after six hours of boating isn’t fun, but it will help you keep your engine performing in peak condition and extend its longevity. Although motor maintenance is a chore, it’s easy for virtually anyone with a tool kit.
Over the next couple of days, we’ll be covering some basic preventative care that should be done after every outing. We’ll also discuss some of the keys for long-term care, how to prepare the motor for storage, and some tips for protecting the unit during transportation. And we’ll go over the basics, including how to select and mix your outboard motor oil properly.